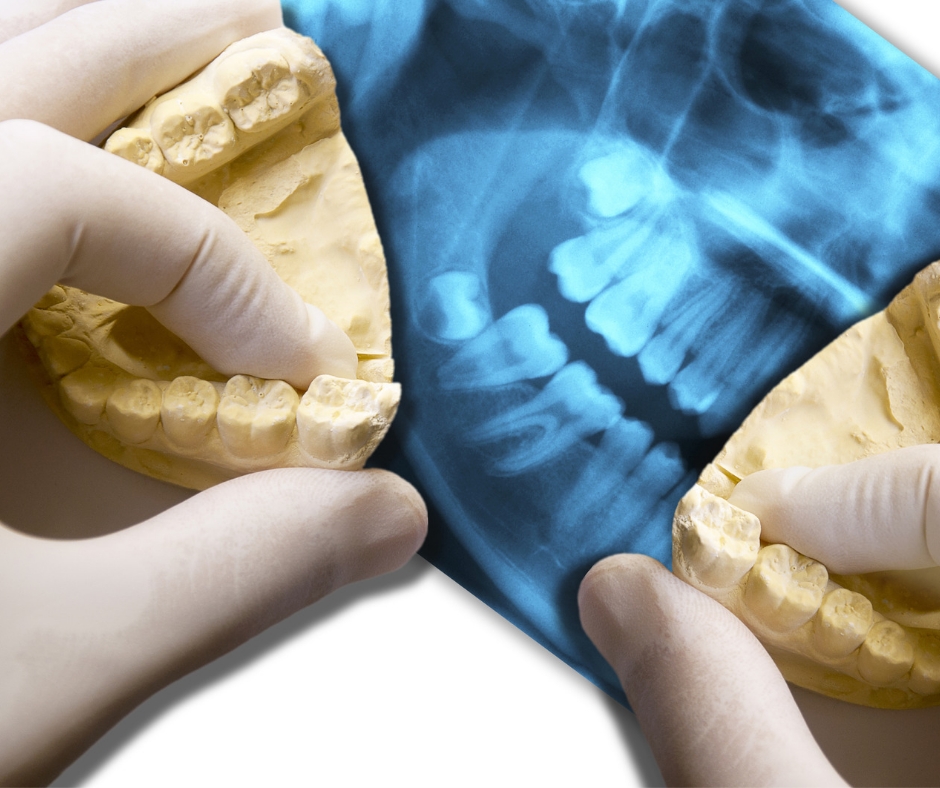
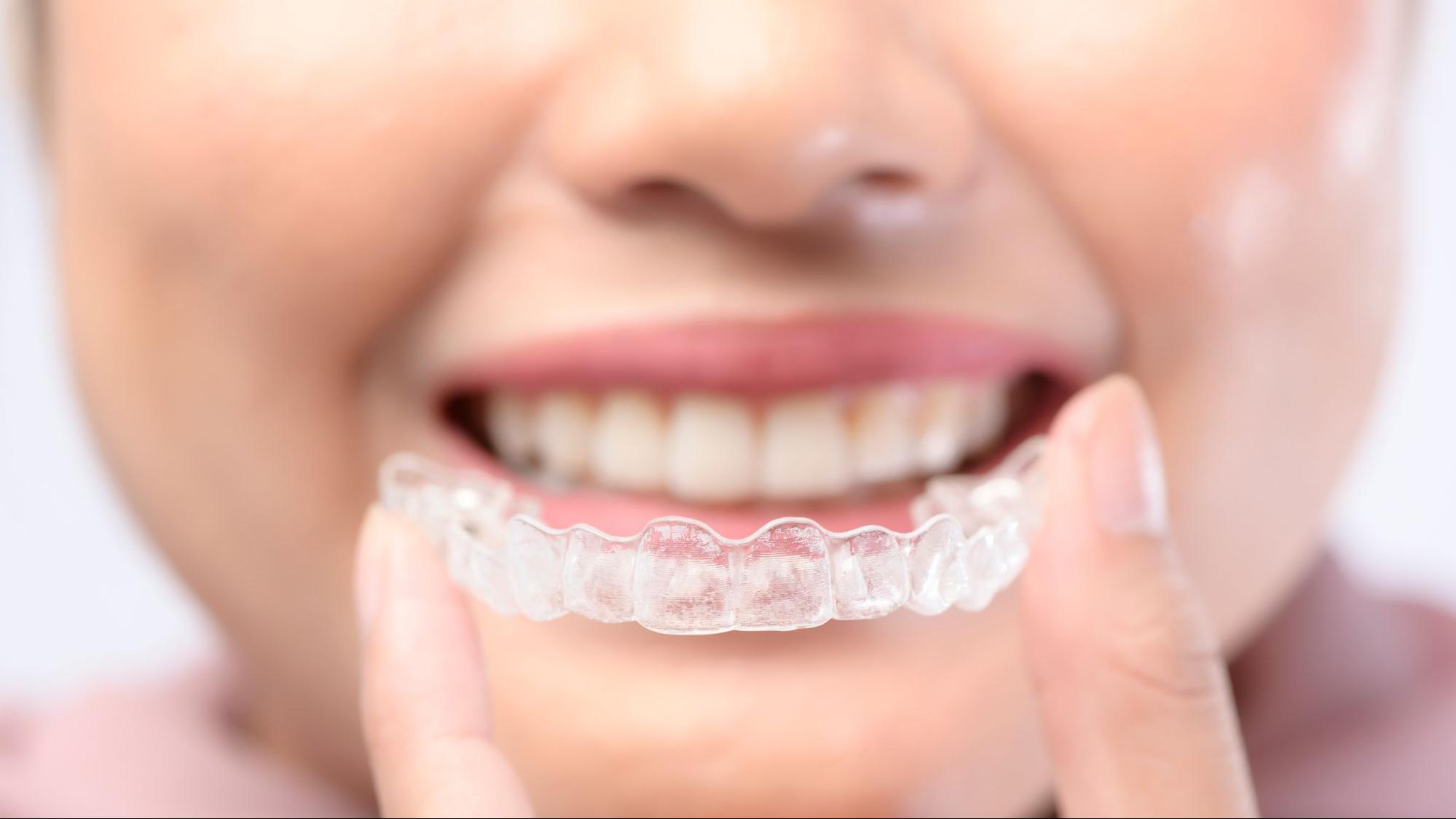
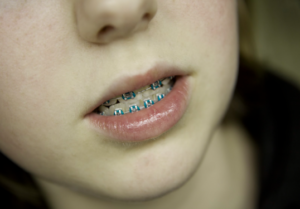One of the important indications of good oral health is that your jaws are aligned properly, and folded over each other.
Having crossbite which is a misalignment of your teeth can affect your bite, speech, and even your facial appearance.
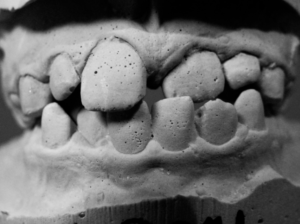
Crossbite
Crossbite is a dental condition that affects the alignment of teeth, which means your teeth don’t fit over each other when you close your mouth.
In this condition, one or more upper teeth fit behind the lower teeth, instead of fitting over them.
This misalignment can occur in the front or back of the mouth.
Crossbite teeth can appear on one or both sides of the jaw.
Types of crossbite
1-Anterior crossbite:
It’s the most noticeable type of crossbite, as it affects the front teeth(incisors) when one or more upper teeth sit behind the lower teeth.
When all top front teeth are fit behind the lower front teeth this condition is called Underbite.
Lingual crossbite
The upper front teeth bite inside the lower front teeth toward the tongue.
Buccal crossbite
The upper front teeth bite outside the lower front teeth toward the cheeks.
2-Posterior crossbite
This type affects the back teeth(molars and premolars), where the upper back teeth fit inside the lower back teeth.
It can be
- Unilateral affects one side of the jaw.
- Bilateral affects both sides of the jaw.
3-Skeletal crossbite
Caused by dissimilarity in size or position of upper and lower jaw.
How do I know that I have a crossbite ?
Some noticeable symptoms can address that you or your child may have Crossbite, but you should consult an orthodontist for a proper diagnosis.
- Uneven bite: The upper and lower teeth don’t meet evenly when you bite down.
- One or more teeth biting inside or outside the opposing arch: This is the most obvious sign of a crossbite.
- Facial asymmetry: In some cases, crossbite can contribute to facial asymmetry, such as a misaligned jawline.
Causes of crossbite
Genetic causes
Crossbite can be inherited, so if one of your parents or other family members has a crossbite, you may inherit it.
Also, genetic causes could be
- Abnormal jaw growth.
- Overcrowded teeth.
- Birth defects such as cleft lip or cleft palate.
Other causes
- Early(premature) loss of baby teeth can affect the normal eruption of permanent teeth causing misalignment.
- Delayed eruption of permanent teeth.
- Prolonged habits such as thumb sucking or the use of a pacifier can exert pressure on the developing teeth causing misalignment.
- An imbalance in the size and position of the upper and lower jaw can contribute to developing crossbites.
So all these factors can contribute to developing crossbite, as it can push the teeth out of their alignment.
What are the consequences of untreated crossbite?
Crossbite isn’t only a cosmetic issue, it can cause serious problems if not treated.
- Appearance of misaligned teeth can affect your confidence.
- Jaw pain: crossbite teeth can stress jaw muscles and joints leading to pain and discomfort.
- Temporomandibular joint disorders.
- Frequent headaches.
- Chewing difficulties: misaligned teeth affect the proper chewing of food, causing potential digestive problems.
- Speech problems.
- Gum diseases, tooth decay: as it’s challenging to keep your misaligned teeth clean, food particles may be trapped in between teeth causing accumulation of plaque and gum diseases.
- In severe cases, it can contribute to skeletal imbalance, affecting facial growth and development.
- Jaw shifting to one side.
- Uneven wear and tear of teeth, potentially causing chipping or fractures of teeth.
- Sleep apnea: misaligned teeth can sit the tongue further back in the mouth, and may block the air passages, making it difficult to breathe.
- Crossbite also can cause teeth grinding, which may contribute to sleep apnea.
- Untreated Crossbite teeth can cause severe dental problems such as tooth loss.
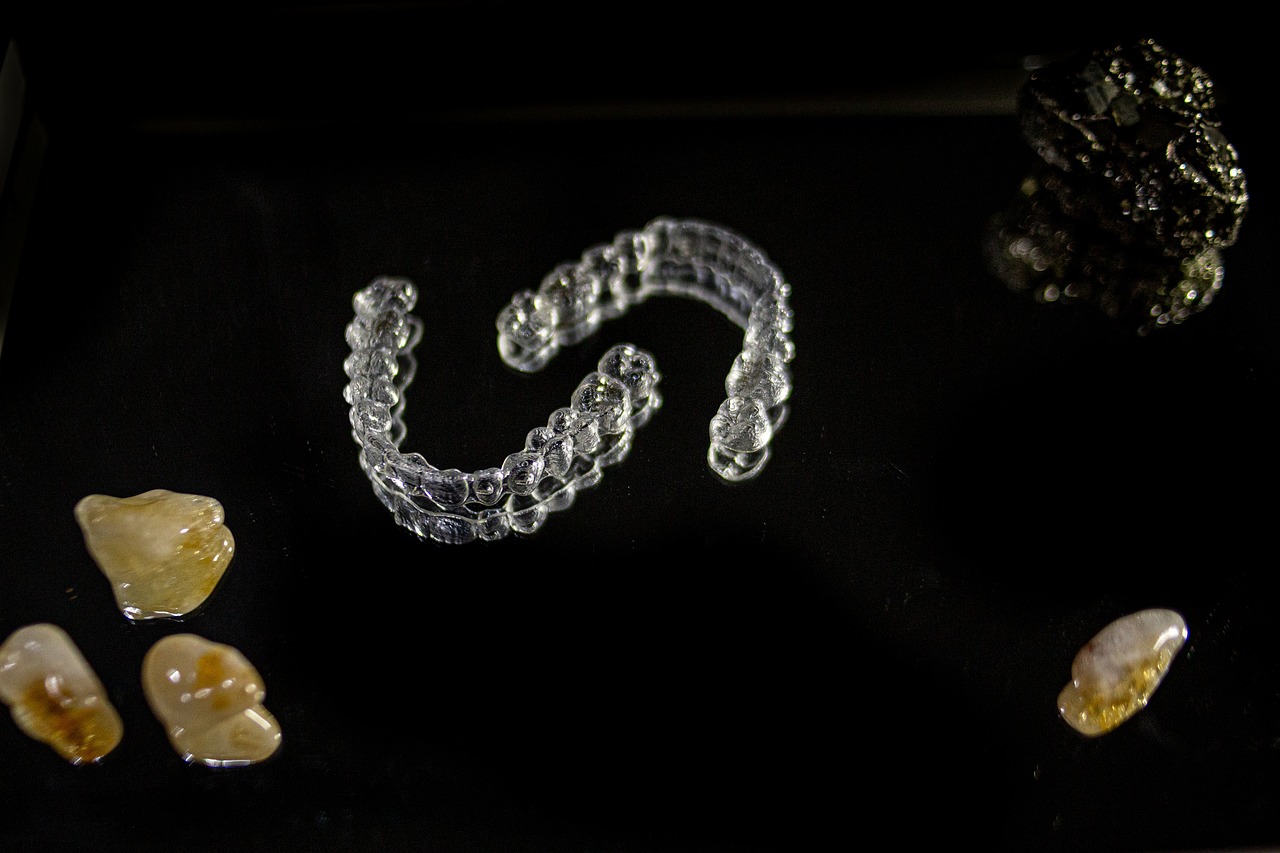
Can clear aligners fix crossbite?

Yes, clear aligners can fix many cases of crossbite teeth, as they gradually shift the teeth to their right position.
Aligners can treat mild to moderate anterior crossbite teeth and some cases of posterior crossbite teeth.
Each crossbite case is unique, so a thorough examination by an experienced orthodontist will determine if aligners are suitable for your case or not.
Other treatment options for crossbite
The treatment period varies between children and adults, it varies between 18 months to 3 years according to the severity of the case.
In children, treatment can start at the age of 10 years when the jaw is still developing.
Braces

Traditional metal braces are an effective method in the treatment of crossbite.
Braces apply gentle pressure on bones and teeth to move teeth gradually to their right position.
Palatal expanders

They used to widen the upper jaw.
Usually used to treat posterior Crossbite.
These expanders gently expand the roof of the mouth to create more space for upper teeth.
Removable palate expanders can be used in adult patients.
Headgear
Sometimes used with braces to help in correcting the position of upper teeth.
Surgery
Used in severe crossbite cases to correct the underlying skeletal issues.
It may include repositioning the upper or lower jaw to achieve proper teeth alignment.
Part of crossbite treatment includes:
Stopping or treating prolonged habits by using a fixed palatal crib(mouth appliance used to stop mouth sucking), this appliance is used if thumb sucking persists after the age of 4 years.
How to choose the right treatment for Crossbite?
The choice of treatment depends on
- the severity of the case.
- Age of the patient: early treatment especially in children is more effective.
- The health condition of your teeth and gums influences the treatment plan.
The bottom line: crossbite not only affects your appearance but also can affect your oral health seriously if not treated. You should consult an experienced orthodontist if you suspect that you or your child have crossbite for proper diagnosis and treatment.